Benvenuti in ACTRIS Italia
Benvenuti in ACTRIS Italia
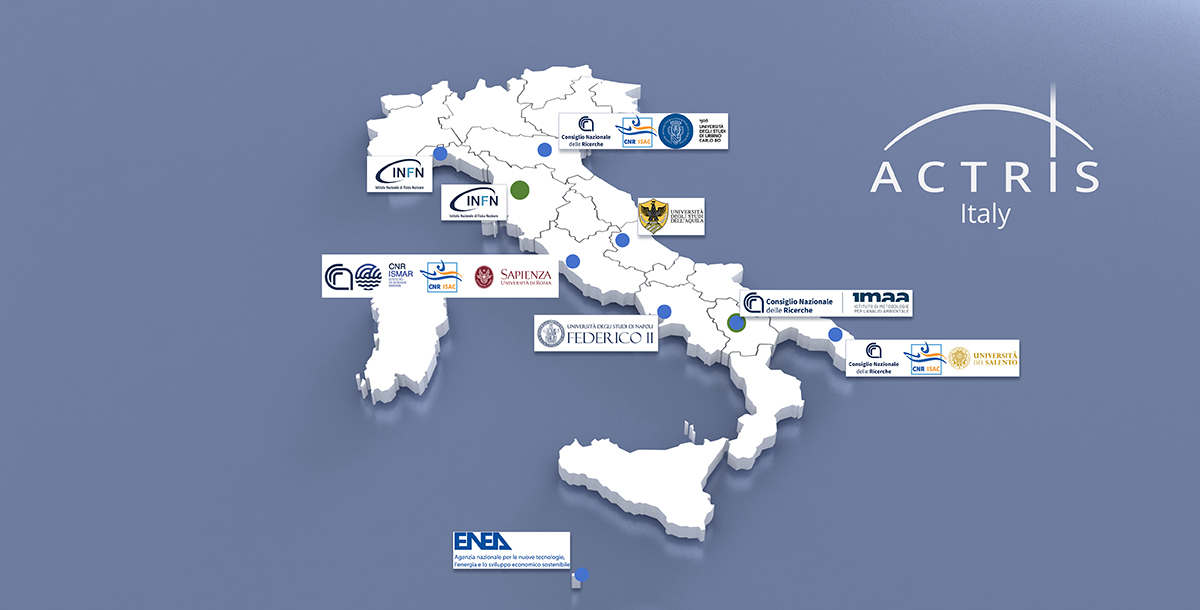
ACTRIS-IT è la componente italiana dell’infrastruttura di ricerca distribuita ACTRIS.
L’infrastruttura di ricerca Aerosol, Clouds and Trace Gases ACTRIS è un’iniziativa paneuropea che coordina le osservazioni e la ricerca scientifica europea su aerosol, nubi e gas in traccia con lo scopo di fornire servizi di alta qualità a un’ampia comunità di utenti pubblici e privati.


ACTRIS Week 2025 will take place in Évora, Portugal
21 Maggio 2025

E’ stato pubblicato il “ACTRIS Community Handbook 2025”
29 Aprile 2025

The ACTRIS Week 2024 was held from November 5-7 in Matera.
12 Novembre 2024

ACTRIS Week 05/07 Nov 2024 – Matera
8 Ottobre 2024
ACTRIS Week 2025 will take place in Évora, Portugal
21 Maggio 2025
E’ stato pubblicato il “ACTRIS Community Handbook 2025”
29 Aprile 2025
The ACTRIS Week 2024 was held from November 5-7 in Matera.
12 Novembre 2024
ACTRIS Week 05/07 Nov 2024 – Matera
8 Ottobre 2024